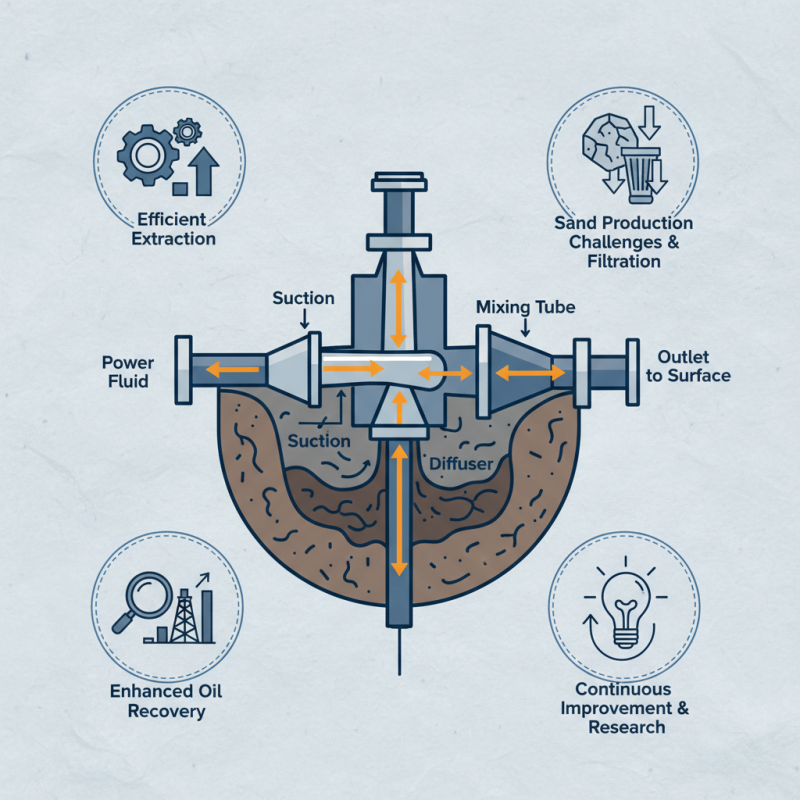
What is a downhole jet pump and how does it work?
The downhole jet pump is a critical component in the oil and gas industry. It plays a vital role in enhanced oil recovery and dewatering processes. According to a recent report by the International Energy Agency, the adoption of jet pump technology has increased by 25% over the last five years. This growth is driven by the need for efficient extraction methods.
Expert Dr. James McCarthy, a noted figure in petroleum engineering, emphasizes the significance of this technology. He states, “The downhole jet pump revolutionizes how we access resources below the surface.” This technology uses high-pressure fluid to create a vacuum, pulling oil and gas to the surface effectively.
The mechanics behind a downhole jet pump are often complex. However, it can face challenges, such as sand production which can damage the system. Continuous improvement and adaptation in the design are necessary. The industry must reflect on these challenges to enhance performance and reliability. Investing in research can lead to more efficient solutions.
What is a Downhole Jet Pump?
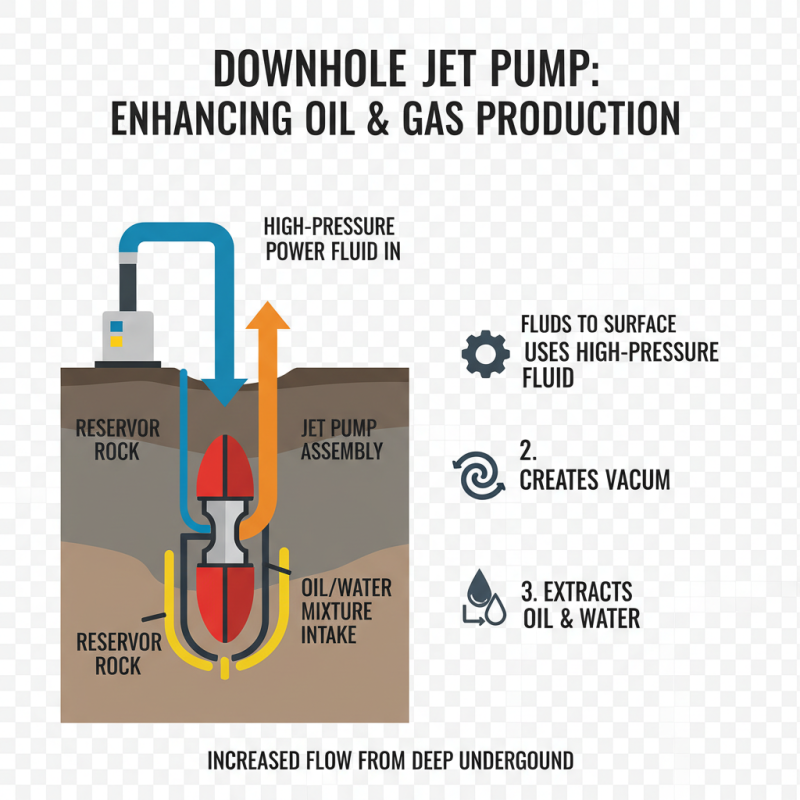
A downhole jet pump is an important tool in oil and gas production. It uses fluid dynamics to enhance fluid flow from deep underground. This pump operates by utilizing high-pressure fluid to create a vacuum, allowing for the extraction of liquids. Typically, these jets are placed within the wellbore, where they can effectively draw oil or water to the surface.
Jet pumps are particularly valuable in low-pressure wells. According to a report by the Society of Petroleum Engineers, these devices can improve extraction rates by up to 30% in certain conditions. These pumps work without moving parts, which reduces maintenance costs. However, the efficiency of a jet pump can vary depending on the fluid's characteristics.
One downside is the reliance on external power to generate the high-pressure fluid. If this supply is disrupted, so is the pump’s effectiveness. Moreover, when considering installation, space and environmental factors must be analyzed closely. In some cases, the cost of installation may not justify the potential benefits. This calls for careful evaluation before deploying a downhole jet pump in any project.
Principle of Operation of Downhole Jet Pumps
Downhole jet pumps are commonly used in oil and gas extraction. Their operation is based on the principle of fluid dynamics. High-pressure fluid is injected through a nozzle, creating a jet. This jet then mixes with the fluid to be lifted. The resulting mixture gains velocity and is pumped to the surface. According to a recent industry report, jet pumps can achieve efficiencies of up to 80% in suitable conditions.
In the design of downhole jet pumps, the size and shape of the nozzle are crucial. A well-optimized nozzle can enhance fluid velocity significantly. Adjusting the nozzle diameter affects performance. Improper sizing can lead to issues, such as reduced efficiency or cavitation. Some reports suggest that minor design flaws can reduce pump performance by as much as 20%. This often goes unnoticed until production declines.
The versatility of downhole jet pumps allows for application in various well conditions. They work effectively in wells with low pressure. However, they may struggle in highly viscous fluids. Operators must monitor their efficiency regularly. Simple adjustments can lead to improved performance and better yields. Continuous evaluation ensures that these systems operate at their best.
Performance of Downhole Jet Pumps at Different Flow Rates
This chart illustrates the performance of a downhole jet pump across various flow rates. The x-axis represents the flow rate in gallons per minute (GPM), while the y-axis shows the efficiency percentage. The data demonstrates how efficiency changes with varying flow rates, highlighting the optimal range for effective operation.
Components of a Downhole Jet Pump System
A downhole jet pump is a vital tool in the oil and gas industry. It operates by using high-pressure fluid to lift hydrocarbons from depths. Understanding its components helps to appreciate its function.
The primary components include the nozzle, mixing chamber, and the venturi. The nozzle injects fluid at high speed, creating a vacuum. This vacuum draws the reservoir fluid into the mixing chamber. Here, the momentum from the injected fluid mixes with the produced fluid to create an effective lifting action. The venturi further accelerates this mixture, allowing it to rise to the surface.
Additionally, there are check valves and fittings ensuring proper flow and direction. Each component plays a unique role. A failure in any part can lead to inefficiency. Regular maintenance is crucial. The balance between pressure and flow is delicate. An operator must monitor these parameters closely for optimal performance. It is a dance of engineering and nature, often requiring adjustments and recalibrations. Effective management of these components can enhance operational productivity significantly.
Applications of Downhole Jet Pumps in Oil and Gas Industry
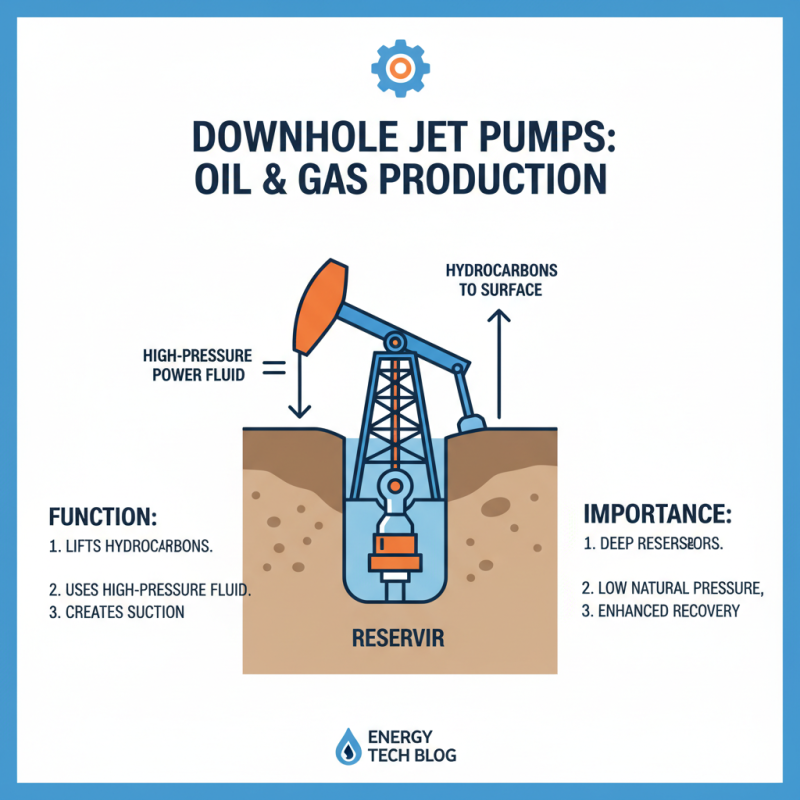
Downhole jet pumps play a crucial role in the oil and gas industry. These systems are useful for lifting hydrocarbons from deep underground reservoirs. Jet pumps use high-pressure fluid to create a suction effect. This is essential when the natural reservoir pressure drops.
These pumps find applications in various scenarios. Workers often use them in both new wells and aging ones. They are effective in enhanced oil recovery methods. This technology helps to maximize production from existing wells. The flexibility of downhole jet pumps allows for adaptation to specific geological conditions. However, not all wells benefit equally from this method.
Despite their advantages, challenges exist. Pump efficiency can vary based on depth and fluid viscosity. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure optimal performance. Operators must evaluate well conditions before installation. By doing so, they can avoid inefficiencies and enhance oil recovery efforts. Adjustments might be necessary over time to maintain optimal function.
Advantages and Limitations of Using Downhole Jet Pumps
Downhole jet pumps are common tools used in oil and water extraction. They rely on high-pressure fluid to create suction, drawing fluids up from deep underground. This method can be very effective. However, not all scenarios benefit from using these pumps.
One advantage is their simplicity. They have fewer moving parts compared to mechanical pumps. This can lead to lower maintenance costs. Additionally, they can operate in various conditions, even in turbulent fluid environments. But this versatility has its limits. Jet pumps may struggle in very viscous fluids. They can also be less efficient at greater depths, where pressure drops affect performance.
Another consideration is their energy usage. While they are often cost-effective initially, energy consumption can add up over time. Operators must assess if the benefits outweigh the costs. This constant evaluation is crucial, especially in fluctuating markets. Understanding these pros and cons helps in making informed choices about downhole jet pump usage.
What is a downhole jet pump and how does it work? - Advantages and Limitations of Using Downhole Jet Pumps
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | A downhole jet pump is a device used to lift water or other fluids from deep within a well using high-pressure fluid jetting. |
| How It Works | It operates by using a high-pressure fluid that is directed through a jet nozzle, creating a vacuum that draws fluids into the pump and up to the surface. |
| Advantages |
|
| Limitations |
|
| Applications |
|
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Right Flo Jet Pump for Your Specific Needs
-

7 Best Ways to Maximize Efficiency with Ultra Jet Pumps
-

Exploring Market Trends: Ultra Jet Pump Innovations at the 138th China Import and Export Fair 2025
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Water Well Jet Pump
-
Why Choose Ultra Jet Pumps for Your Water Needs and What Are Their Benefits
-

10 Best Sucker Rod Pumps for Efficient Oil Extraction in 2023
