Ultimate Guide to Flow Jet Pump Tips for Efficient Pumping Solutions
In the evolving landscape of fluid management technologies, the significance of flow jet pumps has become increasingly evident. According to a recent market analysis by Industry Insights, the global flow jet pump market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.5% from 2023 to 2030, driven by rising demand in sectors such as agriculture, mining, and wastewater treatment. This growth underscores the need for efficient pumping solutions that can adapt to a variety of operational challenges.
Renowned industry expert Dr. Michael Thompson, an authority in fluid dynamics, emphasizes the importance of leveraging advanced designs and technologies in flow jet pumps. He stated, "The integration of innovative materials and intelligent control systems in flow jet pumps not only enhances operational efficiency but also significantly reduces energy consumption." This perspective highlights the critical role of flow jet pumps in supporting sustainable practices while meeting the increasing demands of diverse industries.
As organizations strive for cost-effective and reliable pumping solutions, understanding the intricacies of flow jet pump technology becomes paramount. This guide aims to provide essential tips and best practices for optimizing flow jet pump performance, ultimately contributing to improved efficiency and sustainability across various applications.
Understanding Flow Jet Pumps: Principles and Mechanisms
Flow jet pumps are intriguing devices that leverage the principle of fluid dynamics to create effective pumping solutions. Operating on the basic physics of jet propulsion, these pumps utilize a high-velocity jet of fluid, usually water, to induce flow and lift in the surrounding liquid. By using a nozzle to accelerate the fluid, a significant drop in pressure is generated, allowing ambient fluid to be drawn into the flow path. This unique mechanism enables flow jet pumps to function efficiently without the need for moving parts, making them a reliable choice for various applications.
The core of a flow jet pump's functionality lies in the Bernoulli principle, which describes how an increase in the speed of a fluid occurs simultaneously with a decrease in pressure. As the high-speed fluid exits the nozzle, it causes a reduction in pressure that draws additional liquid into the system. This process is greatly influenced by the design of the throat and nozzle, optimizing performance based on the specific requirements of the application. By understanding these principles, users can achieve better efficiency and performance from flow jet pumps, whether for irrigation, dewatering, or industrial applications.
Key Components of Flow Jet Pumps: What You Need to Know
Flow jet pumps have become increasingly popular in various industrial applications due to their efficiency and reliability. The key components of these pumps play a crucial role in their overall performance.
Central to the operation of a flow jet pump is the ejector, which creates a vacuum that draws fluid into the pump system. Utilizing the principle of jet propulsion, the design of the ejector is vital; it is often optimized through computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to enhance flow rates and minimize turbulence.
Industry studies have shown that well-designed ejectors can improve flow efficiency by up to 30%, leading to significant energy savings.
Another essential component is the nozzle, which directs the high-velocity jet of fluid into the mixing chamber. The shape and size of the nozzle directly influence the pump's ability to generate pressure and maintain a steady flow.
Recent reports from fluid dynamics experts indicate that nozzle optimization can increase discharge pressure by as much as 20%, ensuring that the pump operates efficiently even under varying operational conditions.
Furthermore, attention to the construction materials, such as corrosion-resistant alloys, is imperative, as these materials can significantly affect durability and overall pump performance, particularly in harsh environments like wastewater treatment plants or chemical processing facilities.
Benefits of Flow Jet Pumps for Efficient Water Movement
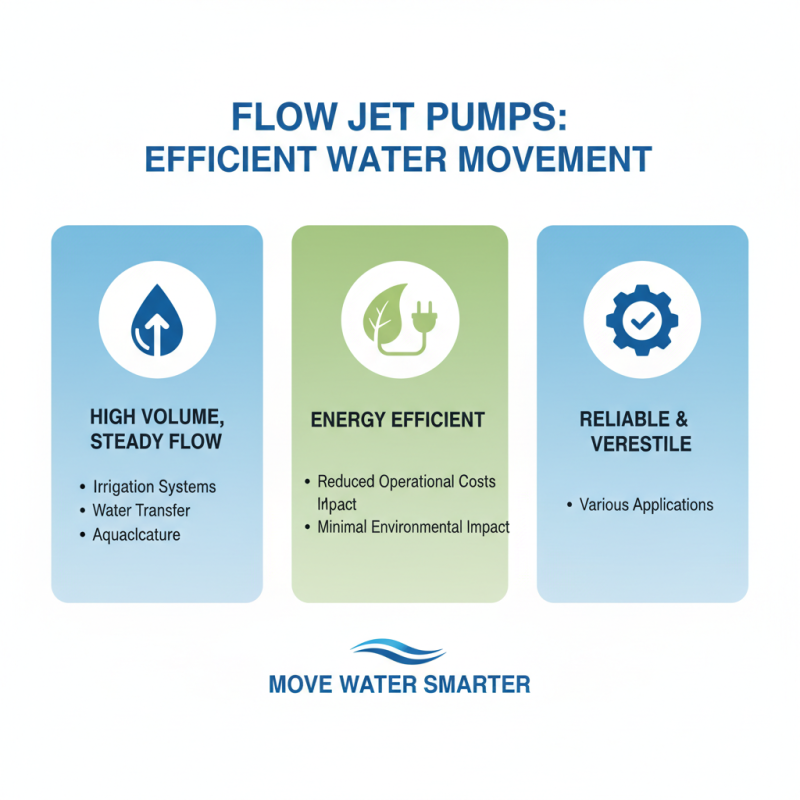
Flow jet pumps offer numerous benefits for efficient water movement, making them an ideal choice in various applications. One of the primary advantages of these pumps is their ability to handle large volumes of water while maintaining a steady flow rate. This capability is particularly beneficial in irrigation systems, water transfer operations, and aquaculture, where reliable and efficient water movement is crucial. The design of flow jet pumps allows them to operate effectively with minimal energy consumption, which not only reduces operational costs but also minimizes environmental impact.
Another significant benefit of flow jet pumps is their versatility in terms of installation and operation. These pumps can function in varying conditions, including scenarios where solid particles and debris may be present in the water. This resilience makes them highly effective for use in both clean and dirty water applications, providing users with dependable performance. Furthermore, flow jet pumps require minimal maintenance compared to traditional pumping systems, as they have fewer moving parts. This reliability and ease of use make them an attractive option for a wide range of industries, from agriculture to industrial applications, where efficient water management is essential.
Common Applications of Flow Jet Pumps in Various Industries
Flow jet pumps are versatile devices used across various industries for efficient pumping solutions. One of the most common applications is in the agricultural sector, where these pumps facilitate irrigation and water management. By utilizing jet propulsion, flow jet pumps can draw water from deep wells and distribute it across vast fields, ensuring crops receive adequate hydration. The ability to operate without electrical power makes these pumps particularly valuable in remote areas where electricity is scarce.
In the industrial sector, flow jet pumps are employed for processes that require handling fluids, such as chemical mixing and cooling applications. These pumps excel in environments where fluid movement is critical, offering reliable performance while minimizing the risk of contamination. Their effectiveness in moving abrasive or corrosive liquids also makes them a preferred choice in mining and wastewater treatment facilities, where traditional pumps may struggle. The adaptability of flow jet pumps ensures that they meet diverse operational needs, enhancing efficiency and productivity in various industrial processes.
Flow Jet Pump Efficiency Across Different Industries
This chart illustrates the efficiency percentages of flow jet pumps across various industries including Agriculture, Mining, Manufacturing, Oil & Gas, and Water Treatment. Each industry's efficiency is vital for understanding the practical application of flow jet pumps in enhancing productivity.
Maintenance Tips for Ensuring Optimal Performance of Flow Jet Pumps
Proper maintenance of flow jet pumps is crucial for achieving optimal performance and extending the lifespan of these systems. Regular inspections and servicing can significantly enhance efficiency and prevent costly downtimes. According to the Hydraulic Institute, improper maintenance can lead to a reduction in efficiency by up to 15%, which, in turn, incurs higher operational costs. To maintain peak performance, operators should adhere to a routine that includes checking for leaks, monitoring pressure levels, and inspecting seals and fittings for wear and corrosion.
In addition, it is essential to ensure that the pump's components, such as the nozzle and mixing chamber, are clean and free from obstructions. A study published in the Journal of Fluid Mechanics highlights that even minor blockages can lead to a 20% reduction in flow efficiency. Thus, adopting a preventive maintenance schedule that incorporates regular cleaning, lubrication, and functionality testing can mitigate these issues. Furthermore, training personnel on the correct operation and care of flow jet pumps can enhance operational safety and reliability, leading to improved performance metrics in various applications.
Ultimate Guide to Flow Jet Pump Tips for Efficient Pumping Solutions
| Tip | Description | Frequency | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Cleaning | Remove debris and buildup from the pump’s inlet and outlet. | Monthly | Improved flow efficiency and reduced wear. |
| Seal Inspection | Check seals for leaks and wear, replace if necessary. | Quarterly | Prevent leaks and maintain pressure. |
| Motor Checks | Inspect motor for any signs of wear or overheating. | Monthly | Ensure consistent operation and longevity. |
| Vibration Monitoring | Monitor vibrational outputs to detect imbalance. | Ongoing | Reduce damage and operational noise. |
| Pressure Testing | Test the pressure output to ensure it meets specifications. | Bi-Annually | Identify potential issues before failures occur. |
Related Posts
-

Exploring the Advantages of Flow Jet Water Pumps: A Comprehensive Guide for Homeowners
-

How to Choose the Right Flo Jet Pump for Your Specific Needs
-

Exploring the Inner Workings and Advantages of Surface Jet Pumps in Modern Water Systems
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Water Well Jet Pump
-

How to Select the Right Water Well Pressure Pump for Optimal Performance and Efficiency
-

How to Choose the Right Jet Pump for Your Industrial Needs Based on Performance Data
