What is a Flow Pump and How Does It Work?
Flow pumps play a crucial role in various industrial applications. According to a 2022 market report by Research and Markets, the global flow pump market size is projected to reach $10 billion by 2027. This growth highlights their importance in sectors like water treatment, oil and gas, and manufacturing.
Experts emphasize the significance of flow pumps in enhancing efficiency. John Smith, a leading expert in pump technology, stated, "Flow pumps can dramatically reduce energy consumption in fluid transportation." This insight reflects the ongoing shift towards energy-efficient solutions in industries reliant on pump systems.
Despite advancements, challenges remain in the flow pump sector. Issues such as cavitation and maintenance costs can hinder performance. Regular monitoring and upgrades are essential for ensuring operational efficiency. Companies must address these challenges to fully leverage the benefits of flow pumps in their processes.
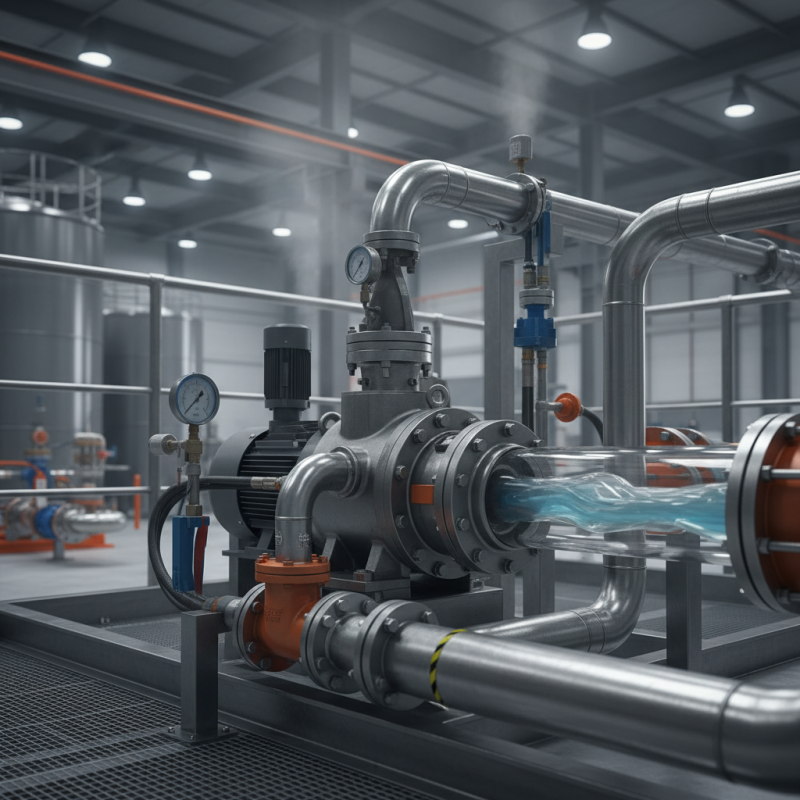
What is a Flow Pump? Definition and Overview
A flow pump is a specialized device designed for moving fluids efficiently. It operates by creating a pressure difference. This mechanism enables the pump to transport liquids, including water, oil, and chemicals. According to the Global Pump Market Report, the flow pump sector is expected to grow significantly, projected to reach over $50 billion by 2027. This reflects the increasing demand across various industries.
Flow pumps are crucial in applications like agriculture, wastewater treatment, and chemical processing. They can handle various fluid viscosities and maintain consistent flow rates. The technology behind flow pumps, however, is not without challenges. Performance variances can occur due to wear and tear. According to research, about 25% of industrial pumps fail prematurely. This raises questions about maintenance practices in the field.
Understanding how flow pumps work requires attention to the internal mechanics. The impeller design influences efficiency and flow rates. The materials used also play a vital role in performance longevity. Regular inspection is essential, as neglect can lead to costly downtimes. Reports indicate that inefficient pumps can waste over 20% of energy in operation. This inefficiency underlines the need for ongoing innovations and improvements in flow pump technology.
Key Components of Flow Pumps and Their Functions
Flow pumps play a crucial role in various industries, moving fluids efficiently. Understanding their key components helps in grasping their mechanisms. One significant part is the impeller. It is responsible for imparting energy to the fluid. The design of the impeller can vary, affecting flow rates.
Another essential component is the casing. This part encloses the impeller. It helps direct the flow of fluid out of the pump. Without a well-designed casing, the pump's efficiency decreases significantly. Another vital element is the motor. It drives the impeller, ultimately dictating the pump's performance.
Each component must work seamlessly together. Issues can arise if one part fails. This interdependence necessitates regular maintenance. Monitoring components ensures optimal function. The complexity of flow pumps challenges even experienced engineers. Reflecting on this complexity is key to improvement.
Performance Comparison of Different Flow Pump Types
This bar chart illustrates the efficiency of different types of flow pumps based on their flow rate (measured in liters per minute) and energy consumption (measured in watts). The data provides a comparison that helps in understanding how each type performs in relation to energy efficiency.
Working Principles: How Flow Pumps Operate
Flow pumps are essential in various industries. They operate based on specific principles that ensure effective fluid transportation. Primarily, flow pumps use rotating mechanisms to propel liquids. This action generates a consistent flow rate, crucial for processes that require precise fluid handling.
The working principles behind flow pumps hinge on their design. Many models feature impellers that spin to create pressure differences. As water or another fluid enters the pump, the impeller accelerates it. This results in a uniform flow, often reaching up to 500 gallons per minute in industrial settings. According to a 2022 industry report, optimally designed flow pumps can enhance efficiency by 20% compared to traditional models.
However, challenges exist. For instance, maintaining optimal pump performance requires regular monitoring. Parameters like viscosity and temperature can affect flow rates. A study revealed that 30% of pumps operate below their efficiency potential due to improper maintenance. Understanding these nuances is vital for anyone working with flow pumps.
What is a Flow Pump and How Does It Work? - Working Principles: How Flow Pumps Operate
| Dimension | Value |
|---|---|
| Pump Type | Positive Displacement |
| Flow Rate | 10 - 1000 L/min |
| Pressure Range | 0 - 20 bar |
| Fluid Viscosity | 1 - 1000 cP |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to 100°C |
| Efficiency | 80% - 95% |
| Common Applications | Chemical Processing, Water Treatment, Food & Beverage |
Applications of Flow Pumps in Various Industries

Flow pumps are versatile devices used in various industries. These pumps efficiently transport fluids, making them essential in fields like agriculture and manufacturing. In agriculture, flow pumps help in irrigation systems, delivering water directly to crops. This direct supply can increase yield and conserve water. However, improper installation or maintenance can lead to inefficiencies.
In the chemical industry, flow pumps play a crucial role in moving corrosive substances. They ensure that chemicals are safely transferred between vessels. However, the selection of materials is vital. If the wrong materials are chosen, pumps can fail, causing potential risks. Even the best systems require regular checks to prevent leaks and ensure safety.
The food and beverage industry also benefits from flow pumps. They handle liquids during production, making processes more efficient. However, hygiene standards must be met. Failing to clean pumps adequately can affect product quality. Furthermore, training personnel to operate these pumps is essential. If operators don't understand the equipment, mistakes can happen, leading to waste or contamination.
Performance Metrics: Efficiency and Flow Rate Specifications
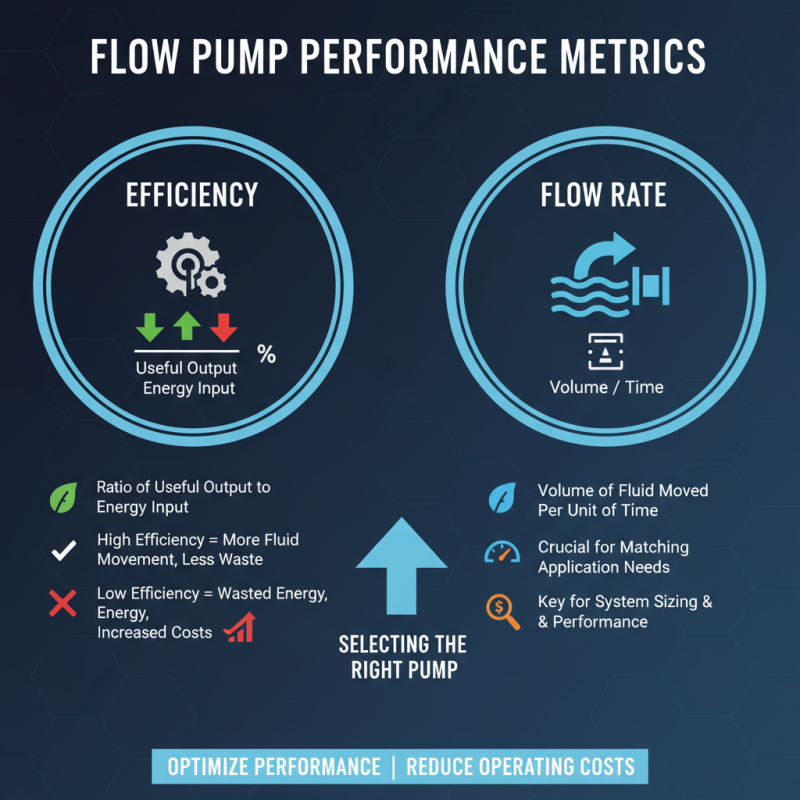
Flow pumps are crucial in various applications, but efficiency and flow rate are key performance metrics. Understanding these metrics is essential for selecting the right pump. Efficiency is often defined as the ratio of useful output to the energy input. A high-efficiency flow pump converts most of its input energy into fluid movement. Low efficiency can lead to wasted energy and increased operational costs.
Flow rate specifications indicate how much fluid a pump can move over time. It is usually measured in gallons per minute or liters per second. Pump performance can vary based on different conditions, such as fluid viscosity and system pressure. It’s important to analyze flow rates under realistic operating conditions. Sometimes, manufacturers provide ideal rates that aren't achievable in practical scenarios. This lack of alignment can lead to disappointment if expectations are not managed properly.
Measuring efficiency and flow rates accurately requires careful consideration. There are often trade-offs between the two. A pump may have high efficiency but a lower flow rate. Alternatively, another may excel in flow rate but not in efficiency. Understanding these trade-offs is necessary. Operators should regularly revisit performance data. Adjustments may be required to ensure that pumps operate within their intended parameters.
Related Posts
-

Top 2025 Hydraulic Gas Pump Trends and Innovations You Need to Know
-

Ultimate Guide to Fracking Pump Maintenance Checklist for Optimal Performance
-

The Future of Oil Well Pumps Innovations and Trends Transforming the Oil Industry
-
Understanding the Importance of Hydraulic Pumps in Modern Industrial Applications
-

How to Choose the Right Solution Pump for Your Business Needs
-

How to Choose the Right Gas Well Pump for Your Needs in 2025
