What is the Functionality of a Hydraulic Fluid Pump in Modern Machinery
In the realm of modern machinery, the functionality of a hydraulic fluid pump plays a pivotal role in enhancing operational efficiency and effectiveness. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global hydraulic pump market is projected to reach USD 11.96 billion by 2025, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2%. This underscores the increasing reliance on hydraulic fluid pumps across various sectors, including construction, manufacturing, and automotive industries. Hydraulic fluid pumps are essential for converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, enabling the smooth operation of hydraulic systems. With advancements in technology, these pumps have become more efficient, compact, and reliable, thus meeting the ever-evolving demands of modern machinery and applications. Understanding the intricacies of hydraulic fluid pumps not only helps in optimizing machinery performance but also contributes to sustained productivity and safety in industrial settings.
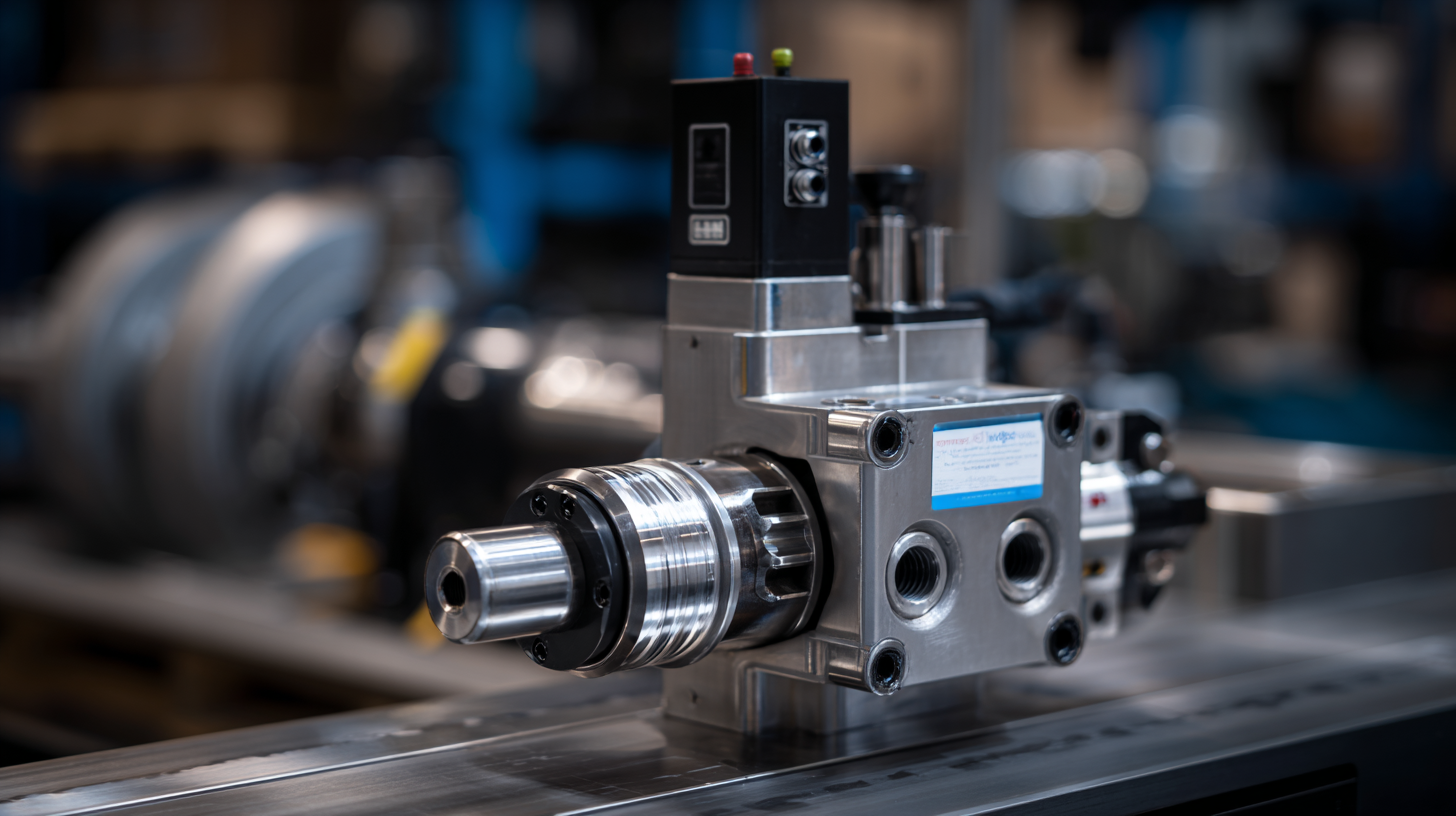
Understanding the Role of Hydraulic Fluid Pumps in Industrial Equipment
Hydraulic fluid pumps play a critical role in the operation of industrial equipment by converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. These pumps generate a flow of hydraulic fluid which transmits power through the system, enabling various machines to perform tasks such as lifting, pressing, and moving heavy loads. The efficiency and reliability of a hydraulic system largely depend on the performance of its fluid pump, making it an essential component in manufacturing, construction, and other sectors that require robust machinery.
In modern machinery, hydraulic fluid pumps are designed to meet specific performance requirements, including pressure and flow rate. By using various types of pumps such as gear, vane, and piston pumps, operators can achieve optimal results tailored to the needs of their equipment. These pumps not only enhance the functionality of machines but also improve safety and precision in operations, allowing for better control and automation in industrial processes. As technology advances, the integration of smart systems with hydraulic fluid pumps continues to elevate their role in maximizing efficiency and reducing downtime in industrial applications.
What is the Functionality of a Hydraulic Fluid Pump in Modern Machinery
| Pump Type | Application | Flow Rate (L/min) | Pressure (Bar) | Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gear Pump | Construction Machinery | 50 | 200 | 85 |
| Piston Pump | Manufacturing | 90 | 300 | 92 |
| Vane Pump | Agricultural Equipment | 70 | 180 | 80 |
| Geared Pump | Automotive | 60 | 150 | 88 |
| Roller Pump | Marine Equipment | 45 | 120 | 84 |
Types of Hydraulic Fluid Pumps: Selection Criteria and Applications
Hydraulic fluid pumps play a pivotal role in modern machinery, enabling efficient power transmission through hydraulic systems. When selecting a hydraulic fluid pump, several criteria must be considered, including the application's specific requirements, flow rate, pressure ratings, and the type of hydraulic fluid being used. Different types of pumps, such as gear, vane, and piston pumps, offer various advantages depending on the operational needs. Gear pumps are popular for their simplicity and reliability, making them ideal for low to medium-pressure applications. In contrast, piston pumps provide high efficiency and are suited for high-pressure applications.
The choice of a hydraulic fluid pump should also take into account the pump's size and weight, as well as the system's overall layout and installation space. Factors like noise levels, maintenance requirements, and operating costs further inform the selection process. For instance, vane pumps are known for their quieter operation and ease of maintenance, which can be beneficial in environments where noise and downtime are critical concerns. Understanding these selection criteria helps engineers and operators choose the right pump type to optimize performance and reliability in their hydraulic systems.
Key Components of Hydraulic Fluid Pumps: How They Work Together
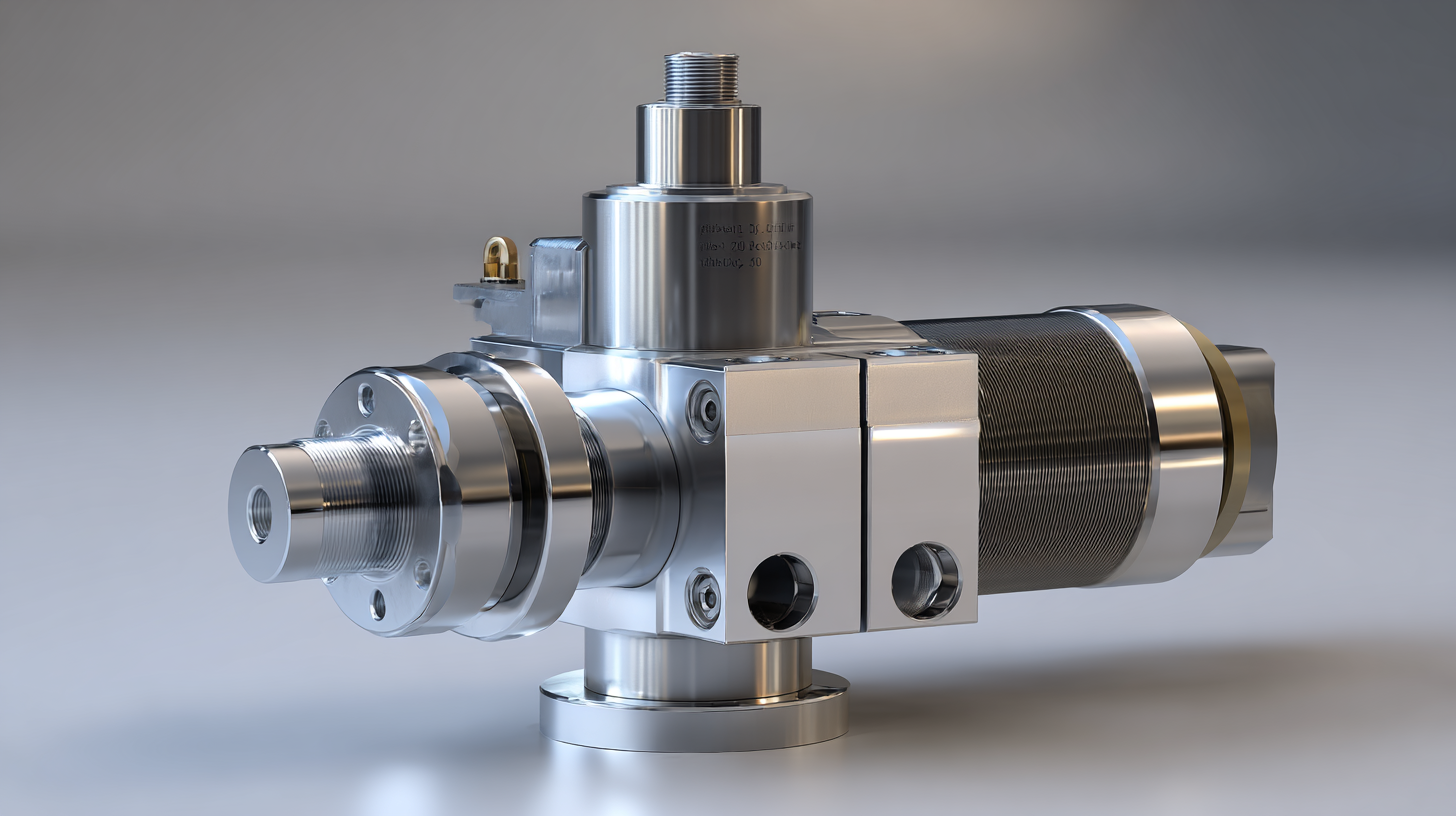 Hydraulic fluid pumps are essential components in modern machinery, driving the efficiency and effectiveness of hydraulic systems across various applications. The primary function of these pumps is to convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, transferring hydraulic fluid that generates motion and power for machines. Key components include the pump body, impellers or pistons, and valves, which work in tandem to create and regulate flow. The recent surge in demand for energy-efficient hydraulic solutions highlights the importance of continuous innovation in pump designs, promoting sustainability, and reducing operational costs.
Hydraulic fluid pumps are essential components in modern machinery, driving the efficiency and effectiveness of hydraulic systems across various applications. The primary function of these pumps is to convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, transferring hydraulic fluid that generates motion and power for machines. Key components include the pump body, impellers or pistons, and valves, which work in tandem to create and regulate flow. The recent surge in demand for energy-efficient hydraulic solutions highlights the importance of continuous innovation in pump designs, promoting sustainability, and reducing operational costs.
Tips: To improve the performance of hydraulic fluid pumps, consider integrating oil condition monitoring sensors. These sensors offer real-time insights into the oil's health, allowing for timely maintenance and reduced downtime. Additionally, adopting biodegradable hydraulic fluids not only supports environmental initiatives but also enhances pump longevity.
The collaboration of electric prime movers with hydraulic systems is increasingly significant, driving advancements in mobile machinery. This integration aims to achieve smarter and more efficient machines capable of meeting rigorous efficiency standards. As technology continues to evolve, the hydraulic fluid pump's role remains pivotal, adapting to new developments in data center cooling and mobile hydraulics, ensuring that modern machinery functions with precision and sustainability.
Performance Metrics: Measuring Efficiency and Output of Hydraulic Pumps
The performance metrics of hydraulic pumps are crucial in assessing their efficiency and output in modern machinery. According to the Hydraulic Institute, the efficiency of hydraulic pumps can significantly influence operational costs, with high-efficiency pumps achieving upwards of 90% efficiency under optimal conditions. By measuring parameters such as volumetric efficiency, mechanical efficiency, and overall pump efficiency, manufacturers can ensure that the pumps deliver the required flow and pressure with minimal energy loss. These metrics not only help in maximizing performance but also in minimizing environmental impacts, as more efficient pumps consume less power.
Tips: Regular maintenance and monitoring of hydraulic pumps can enhance performance metrics. Implementing a preventive maintenance schedule can help in identifying wear and tear, which is crucial for sustaining high efficiency levels. Additionally, using advanced monitoring systems can provide real-time data on the pump’s performance, enabling timely adjustments to optimize output.
Moreover, understanding the impact of fluid dynamics within the hydraulic system can further improve pump performance. Research shows that optimizing the fluid viscosity and selecting the right type of hydraulic fluid can improve the overall efficiency of the system. For instance, using synthetic oils can reduce friction and heat generation, catering to higher performance standards as recommended by major equipment manufacturers in industry reports.
Maintaining Hydraulic Fluid Pumps: Best Practices for Longevity and Reliability
Maintaining hydraulic fluid pumps is crucial for ensuring their longevity and reliability in modern machinery. According to a report from the Hydraulic Institute, improper maintenance can lead to a decrease in pump efficiency by up to 20%, significantly impacting overall system performance. Regular inspections of hydraulic fluid levels, leak checks, and monitoring for unusual noises or vibrations are essential practices. Implementing a scheduled maintenance program not only helps in early detection of potential issues but also maximizes the pump's operational lifespan.

Related Posts
-
How to Effectively Maintain Your Hydraulic Gas Pump for Optimal Performance
-

Ultimate Guide to Fracking Pump Maintenance Checklist for Optimal Performance
-

Understanding the Mechanism of Sucker Rod Pumps in Oil Extraction
-

How to Choose the Right Well Pump for Your Water Needs
-

5 Best Artificial Lift Pumps Revolutionizing Oil Recovery: Boost Efficiency and Cut Costs
-

Exploring Innovative Alternatives to Flo Jet Pumps for Efficient Fluid Management
