What is an Industrial Pump and How Does It Work in Various Applications
Industrial pumps are integral components in various sectors of the manufacturing and processing industries, facilitating the movement of fluids across a wide range of applications. According to a recent report by the Global Market Insights, the industrial pump market is expected to surpass USD 80 billion by 2026, driven by rising demand in industries such as water and wastewater treatment, oil and gas, and chemical processing. These pumps not only aid in fluid transfer but also play a crucial role in ensuring operational efficiency and safety in complex industrial systems.
In essence, industrial pumps function by converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, enabling the transport of liquids, slurries, and gases. As industries continue to evolve, the need for innovative pumping solutions has become more critical, particularly with increasing environmental regulations and sustainability goals. As per the latest research from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, advancements in pump design and technology have led to significant improvements in energy efficiency, reducing operational costs and minimizing environmental impact. In this dynamic landscape, understanding the various types of industrial pumps and their applications is essential for optimizing performance and achieving economic sustainability in industrial operations.

What is an Industrial Pump?
Industrial pumps are mechanical devices designed to move fluids or slurries through pipelines by converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. These pumps play a crucial role in various industries, including oil and gas, manufacturing, water treatment, and chemical processing. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global industrial pump market was valued at approximately $68 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach about $108 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 7.5% over the forecast period. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for efficient fluid handling solutions across various sectors.
The working principle of an industrial pump relies on its design and the type of pump used—whether it is centrifugal, positive displacement, or submersible. For instance, centrifugal pumps use rotational energy to propel fluid, making them ideal for low-viscosity liquids and higher flow rates. In contrast, positive displacement pumps, which trap a fixed amount of liquid and force it into the discharge pipe, are often used for high-viscosity fluids requiring greater pressure. A market analysis highlighted that centrifugal pumps dominate the sector, accounting for over 50% of total pump sales, due to their versatility and efficiency in numerous applications, from irrigation systems to chemical processing facilities.
Types of Industrial Pumps and Their Functions
Industrial pumps are critical components used across various sectors, serving a multitude of functions depending on their design and application. The primary types of industrial pumps include centrifugal pumps, positive displacement pumps, peristaltic pumps, and diaphragm pumps, each suited for specific tasks. Centrifugal pumps, which utilize rotational energy to move fluids, are widely employed in water supply and sewage treatment, accounting for nearly 80% of the pumps used in industrial applications, according to a report by the Hydraulic Institute.
Positive displacement pumps, on the other hand, function by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing it through the pump system, making them ideal for applications that require high pressure and precise flow rates, such as in oil and gas industries. They can handle a variety of fluids, including viscous materials and slurries, thus making them versatile for a range of processes. In specialized applications, peristaltic pumps offer the advantage of gentle pumping action suitable for handling shear-sensitive fluids, while diaphragm pumps are favored for their ability to pump corrosive fluids safely.
The versatility of industrial pumps is also highlighted in the global market, projected to reach USD 70 billion by 2025, as industries continue to adopt advanced pumping solutions to improve efficiency and reduce downtime. As the demand for reliable and efficient fluid transfer systems grows, understanding the specific functions of each type of pump becomes essential for optimizing industrial operations.
Industrial Pump Types and Their Applications
Principles of Operation for Various Industrial Pumps
Industrial pumps are essential components in various sectors, designed to transport fluids and facilitate numerous processes. Their operation is based on fundamental principles that differ among various types, including centrifugal pumps, positive displacement pumps, and diaphragm pumps. Centrifugal pumps utilize rotational energy from impellers to increase fluid velocity, converting kinetic energy into pressure energy as the fluid exits the pump. These pumps are widely used in applications requiring high flow rates, such as water supply and chemical processing.
On the other hand, positive displacement pumps operate by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing it into the discharge pipe. This type includes gear pumps, screw pumps, and diaphragm pumps, and is ideal for applications that require precise flow rates at high pressures, such as in hydraulic systems. Diaphragm pumps are particularly effective for handling corrosive or viscous fluids, as their flexible membranes provide gentle pumping action while minimizing flow shear. Each pump type offers distinct advantages based on the fluid characteristics, required flow rate, and operational pressures, showcasing the versatility and critical role of industrial pumps across various industries.
Applications of Industrial Pumps in Different Industries
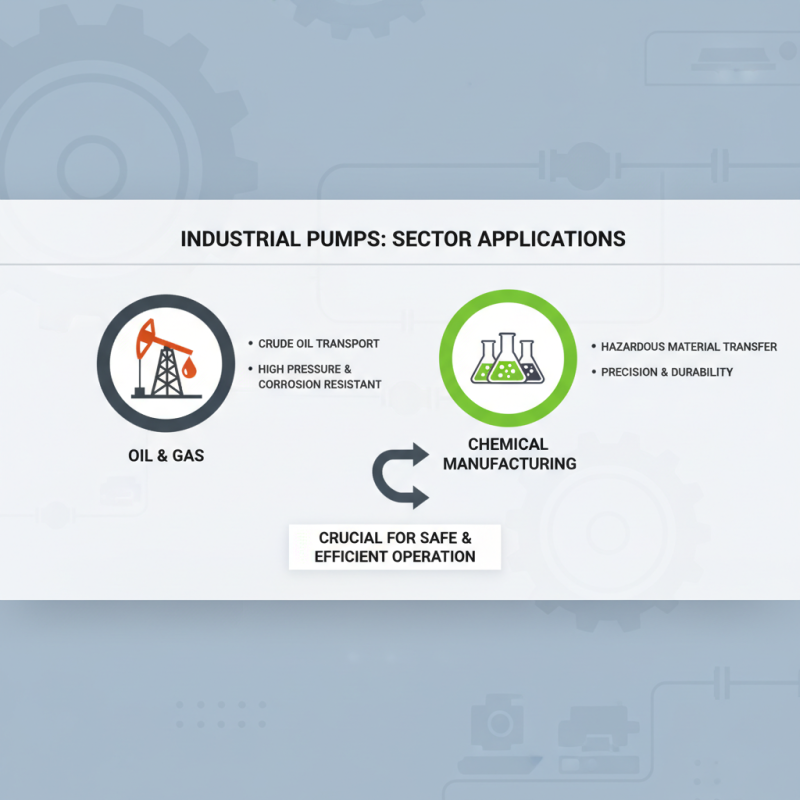
Industrial pumps play a crucial role across various sectors, each with unique applications tailored to specific needs. In the oil and gas industry, for instance, pumps are utilized for transporting crude oil from extraction sites to refineries. These pumps require robust construction to handle high pressures and corrosive substances, ensuring safe and efficient operation over long distances. Additionally, the chemical manufacturing sector relies on pumps to move hazardous materials through various processes, where precision and durability are paramount to maintain product integrity and worker safety.
In the water treatment industry, industrial pumps are essential for processes like filtration and chemical dosing. They help in managing water supply systems, ensuring that clean water reaches communities while efficiently handling wastewater. In agriculture, pumps are integral for irrigation systems, facilitating water distribution necessary for crop cultivation. This versatility highlights the importance of industrial pumps, as they contribute significantly to the functionality and efficiency of different processes, ultimately supporting economic growth and infrastructure development in diverse industries.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Industrial Pumps
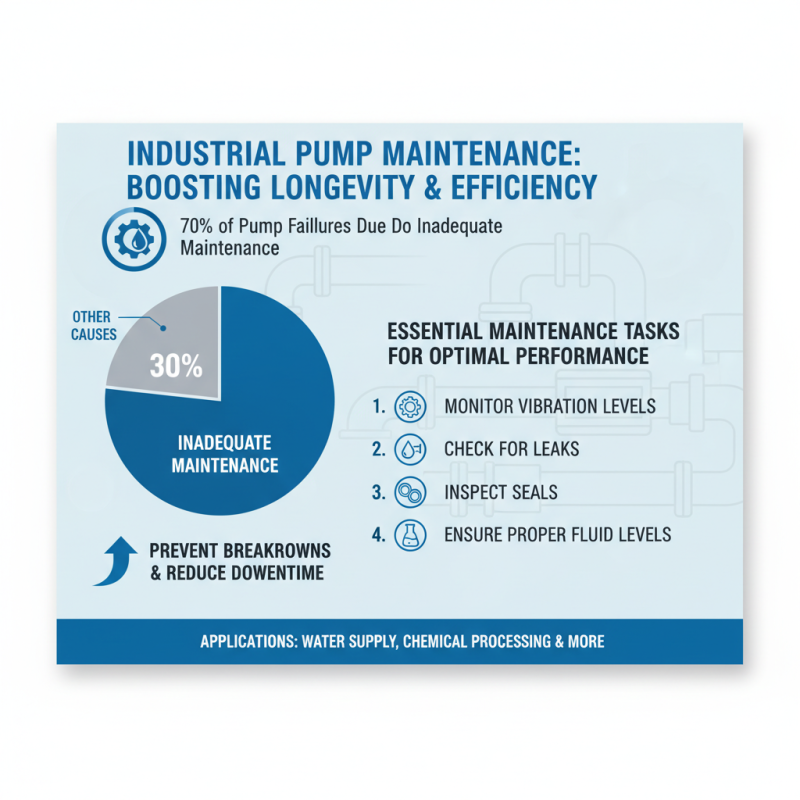
Proper maintenance and troubleshooting of industrial pumps are crucial for ensuring their longevity and operational efficiency. According to a report from the Hydraulic Institute, approximately 70% of pump failures are attributed to inadequate maintenance practices. This highlights the necessity for regular inspections and routine servicing, which can prevent unexpected breakdowns and reduce downtime. Essential maintenance tasks include monitoring vibration levels, checking for leaks, inspecting seals, and ensuring proper fluid levels, which can enhance the pump's performance across various industrial applications, from water supply systems to chemical processing.
When it comes to troubleshooting, understanding common issues is vital. For instance, issues such as cavitation, seal leakage, or mechanical failures can result from improper installation or inadequate maintenance. A study by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers indicates that addressing these problems promptly can save companies up to 30% in repair costs and significantly boost productivity. Utilizing predictive maintenance technologies, such as sensors and condition monitoring systems, allows for real-time diagnostics, enabling operators to act swiftly before minor problems escalate into major failures. Ensuring that maintenance staff is well-trained in recognizing symptoms of failure and thorough troubleshooting can further improve pump reliability and efficiency.
Related Posts
-

Why Industrial Pumps Are Essential for Efficient Process Engineering in Manufacturing Industries
-

2025 Top 5 Industrial Pumps: Best Picks for Efficiency and Performance
-

Streamlining Efficiency: Innovative Solutions for Gas Well Pump Operations in Oil and Gas Industry
-

Understanding the Benefits of a Well Pressure Pump for Your Home Water Supply
-

Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Oil Jet Pump for Your Industry Needs
-
How to Select the Right Hydraulic Pump for Your Project Needs
