How to Select the Right Hydraulic Pump for Your Project Needs
Selecting the right hydraulic pump for your project needs is a critical decision that can influence the efficiency and effectiveness of your operations. According to a recent industry report by ResearchAndMarkets, the global hydraulic pump market is expected to reach $15 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 4.5%. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for hydraulic systems in construction, manufacturing, and other industrial applications. As businesses continue to expand, understanding the specific requirements of hydraulic pumps becomes essential for optimizing performance and ensuring reliability.
Industry expert Dr. Emily Sanchez, a leading authority in fluid power technology, emphasizes the significance of proper selection by stating, "Choosing the right hydraulic pump not only improves system efficiency but also extends the lifespan of your equipment." Her insights highlight the importance of evaluating factors such as flow rate, pressure requirements, and compatibility with existing systems when selecting a hydraulic pump. By considering these variables, engineers and project managers can make informed choices that align with their operational goals, ultimately leading to enhanced productivity and reduced operational costs.

Factors to Consider When Choosing a Hydraulic Pump for Your Project
When selecting the right hydraulic pump for your project, several critical factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Firstly, understanding the required flow rate and pressure for your specific application is essential. The flow rate, typically measured in gallons per minute (GPM), determines how quickly fluid will move through the system. Likewise, the pressure requirement indicates the system's ability to perform work against resistance. Ensuring that the hydraulic pump meets these specifications is vital to achieving desired outcomes while preventing potential equipment failure.
Another important consideration is the working environment in which the hydraulic pump will operate. Factors such as ambient temperature, humidity, and exposure to contaminants can significantly impact pump performance and longevity. Selecting materials resistant to corrosion and wear can enhance durability in harsh conditions. Additionally, the pump's size and weight should align with the available space and mobile requirements of the project. Evaluating these criteria can guide you towards a hydraulic pump that meets the unique demands of your application, ultimately contributing to project success.
Hydraulic Pump Selection Factors
Understanding Different Types of Hydraulic Pumps and Their Applications
When selecting the right hydraulic pump for a specific project, it's essential to understand the various types of hydraulic pumps and their respective applications. Hydraulic pumps are primarily categorized into two types: positive displacement pumps and dynamic pumps. Positive displacement pumps, such as gear, piston, and vane pumps, provide a consistent flow regardless of the pressure, making them ideal for high-pressure applications. According to a recent market report, the global hydraulic pump market is projected to reach $15 billion by 2028, with a significant demand for positive displacement pumps in sectors such as construction and mining, where equipment reliability and performance are critical.
Dynamic pumps, on the other hand, include centrifugal pumps that are more suited for low-viscosity fluids and applications requiring high flow rates rather than high pressure. These pumps are typically utilized in industrial processes where large volumes of fluid need to be moved efficiently. The increasing need for automated and efficient fluid management systems in manufacturing has led to a forecasted growth of 4.5% in the centrifugal pump segment over the next five years. Understanding these distinctions is vital for engineers and project managers to ensure the optimal performance of hydraulic systems tailored to their specific operational requirements.
Assessing Flow Rate and Pressure Requirements for Efficient Operation
When selecting a hydraulic pump for your project, understanding the flow rate and pressure requirements is crucial for efficient operation. The flow rate, measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per minute (LPM), determines how quickly hydraulic fluid is delivered throughout the system. Assessing your project’s demand will help identify the ideal flow rate. If the flow rate is too low, your machinery may underperform, while an excessively high flow rate can cause unnecessary wear and increased energy consumption.
Pressure requirements should not be overlooked either. The pressure rating, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI) or bar, indicates the maximum force the pump can deliver. It’s essential to match the pressure capabilities of the pump with the operating requirements of your hydraulic system. Choosing a pump with insufficient pressure may lead to system failure or inefficiency, whereas one that far exceeds your needs can lead to wasted resources and potential safety hazards.
**Tips:** Always calculate the total system requirements, including any losses due to friction or elevation. Additionally, consider environmental factors, such as temperature and fluid type, which can impact pump performance. Lastly, consult with professionals or use simulation tools to validate your selections, ensuring that your hydraulic system operates at peak efficiency.
How to Select the Right Hydraulic Pump for Your Project Needs
| Pump Type | Max Flow Rate (GPM) | Max Pressure (PSI) | Efficiency (%) | Weight (lbs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gear Pump | 15 | 2500 | 80 | 50 |
| Vane Pump | 20 | 3000 | 85 | 60 |
| Piston Pump | 25 | 4000 | 90 | 70 |
| Diaphragm Pump | 10 | 1500 | 75 | 45 |
| Electric Pump | 30 | 5000 | 95 | 75 |
Evaluating Efficiency Ratings and Energy Consumption of Hydraulic Pumps
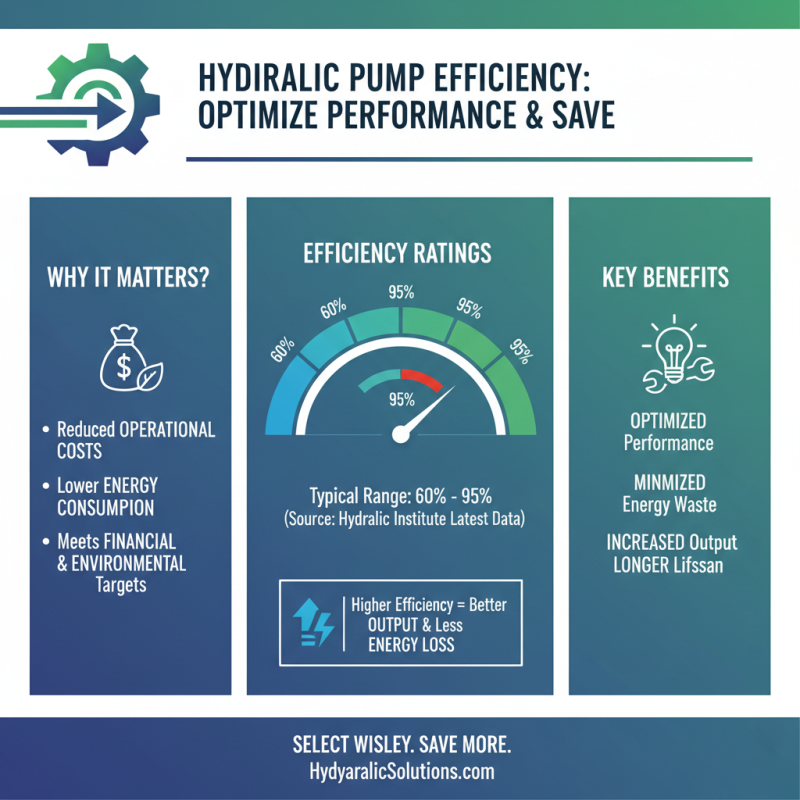
When selecting a hydraulic pump for your project, evaluating efficiency ratings and energy consumption is crucial for optimizing performance and reducing operational costs. According to the Hydraulic Institute's latest data, hydraulic pumps can achieve efficiency ratings between 60% to 95%, depending on their design and application. A pump with a higher efficiency rating not only translates to better output but also minimizes energy losses, which is essential in meeting both financial and environmental targets.
Energy consumption is a significant consideration as it directly impacts the total cost of ownership. A study by the U.S. Department of Energy reveals that hydraulic systems can account for up to 20% of a facility’s energy consumption. Thus, choosing a pump with a lower energy consumption profile can lead to substantial savings over its lifespan. It's essential to examine the pump's specific energy consumption (SEC) data, as it gives insight into how much energy is required to produce a unit of flow. Pumps that operate within a range of less than 0.5 kWh per cubic meter of hydraulic fluid handled are generally considered to be energy-efficient, allowing for a more sustainable operation while still meeting the desired performance levels.
Selecting the Right Materials for Durability and Reliability in Pump Design
When selecting hydraulic pumps, the choice of materials plays a crucial role in ensuring durability and reliability in pump design. The materials used must withstand the operational stresses and environmental conditions to prevent premature failure. Commonly used materials include various grades of steel, aluminum, and specialized alloys that resist corrosion and wear. The choice of material should align with the fluid being pumped, as certain fluids may react with specific metals, leading to degradation or contamination.
Moreover, the manufacturing processes and treatments applied to the materials also influence their performance. For instance, materials that undergo surface hardening or coatings can enhance their resistance to friction and corrosion, extending the pump's lifespan. Additionally, factors such as the pump's operating temperature and pressure must be considered when selecting materials, as they must maintain structural integrity under varying conditions. Understanding these material properties and their interactions with the operational environment is essential for engineers and designers aiming for efficient and lasting pump functionality.
Related Posts
-
What is the Functionality of a Hydraulic Fluid Pump in Modern Machinery
-
20 Best Hydraulic Gas Pumps for Unmatched Performance in 2023
-
Understanding the Importance of Hydraulic Pumps in Modern Industrial Applications
-
Why Choose a Hydraulic Oil Pump: Key Benefits and Features Explained
-

7 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Hydraulic Oil Pump for Your Needs
-

Understanding the Mechanism of Sucker Rod Pumps in Oil Extraction
